–аспознавание дорожных знаков с помощью CNN: »нструменты дл€ препроцессинга изображений |
ѕривет, ’абр! ѕродолжаем серию материалов от выпускника нашей программы Deep Learning, ирилла ƒанилюка, об использовании сверточных нейронных сетей дл€ распознавани€ образов Ч CNN (Convolutional Neural Networks)
«а последние несколько лет сфера компьютерного зрени€ (CV) переживает если не второе рождение, то огромный всплеск интереса к себе. ¬о многом такой рост попул€рности св€зан с эволюцией нейросетевых технологий. Ќапример, сверточные нейронные сети (convolutional neural networks или CNN) отобрали себе большой кусок задач по генерации фич, ранее решаемых классическими методиками CV: HOG, SIFT, RANSAC и т.д.
ћаппинг, классификаци€ изображений, построение маршрута дл€ дронов и беспилотных автомобилей Ч множество задач, св€занных с генерацией фич, классификацией, сегментацией изображений могут быть эффективно решены с помощью сверточных нейронных сетей.

MultiNet как пример нейронной сети (трех в одной), которую мы будем использовать в одном из следующих постов. »сточник.
ѕредполагаетс€, что читатель имеет общее представление о работе нейронных сетей. ¬ сети есть огромное количество постов, курсов и книг на данную тему. примеру:
—овет: чтобы убедитьс€ в том, что вы владеете основами нейронных сетей, напишите свою сеть с нул€ и поиграйте с ней!
¬место того, чтобы повтор€ть основы, данна€ сери€ статей фокусируетс€ на нескольких конкретных архитектурах нейронных сетей: STN (spatial transformer network), IDSIA (сверточна€ нейросеть дл€ классификации дорожных знаков), нейросеть от NVIDIA дл€ end-to-end разработки автопилота и MultiNet дл€ распознавани€ и классификации дорожной разметки и знаков. ѕриступим!
“ема данной статьи Ч показать несколько инструментов дл€ предобработки изображений. ќбщий пайплайн обычно зависит от конкретной задачи, € же хотел бы остановитьс€ именно на инструментах. Ќейросети Ч совсем не те магические черные €щики, какими их люб€т преподносить в медиа: нельз€ просто вз€ть и Ђзакинутьї данных в сетку и ждать волшебных результатов. ѕо правилу shit in Ч shit out в лучшем случае, вы получите score хуже на несколько пунктов. ј, скорее всего, просто не сможете обучить сеть и никакие модные техники типа нормализации батчей или dropout вам не помогут. “аким образом, работу нужно начинать именно с данных: их чистки, нормализации и нормировки. ƒополнительно стоит задуматьс€ над расширением (data augmentation) исходного картиночного датасета с помощью аффинных преобразований типа вращени€, сдвигов, изменени€ масштаба картинок: это поможет снизить веро€тность переобучени€ и обеспечит лучшую инвариантность классификатора к трансформаци€м.
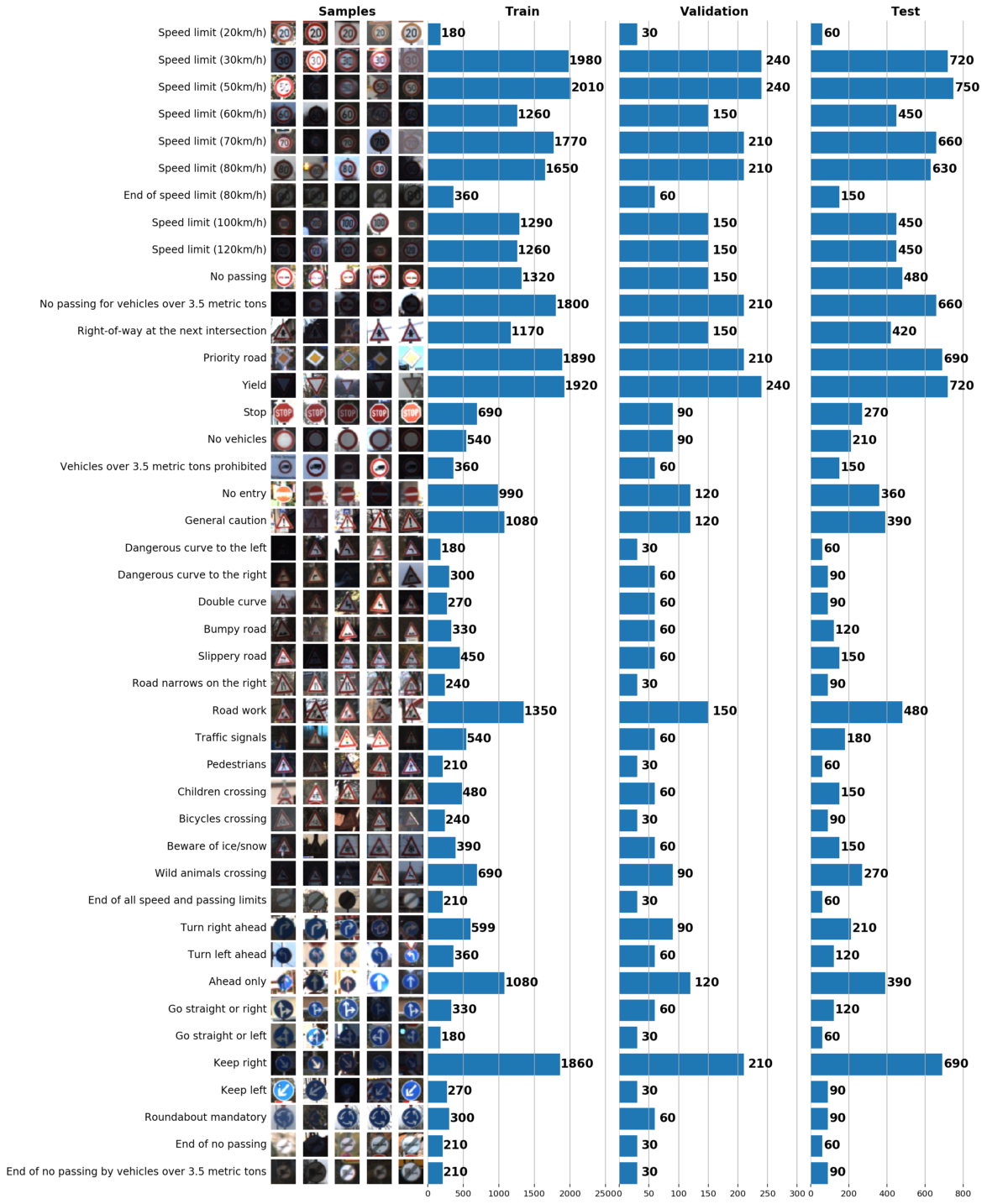
¬ рамках этого и следующего постов мы будем использовать GTSRB Ч датасет по распознаванию дорожных знаков в √ермании. Ќаша задача Ч обучить классификатор дорожных знаков, использу€ размеченные данные из GTSRB. ¬ общем случае, лучший способ получить представление об имеющихс€ данных Ч построить гистограмму распределени€ train, validation и/или test наборов данных:
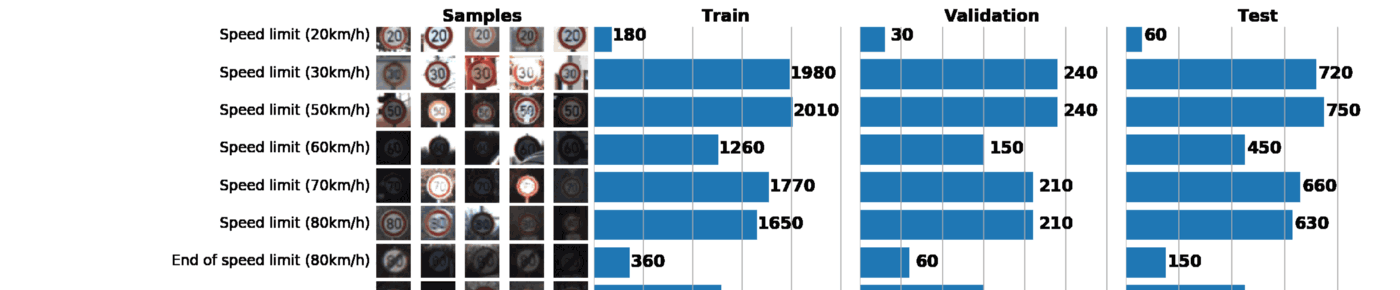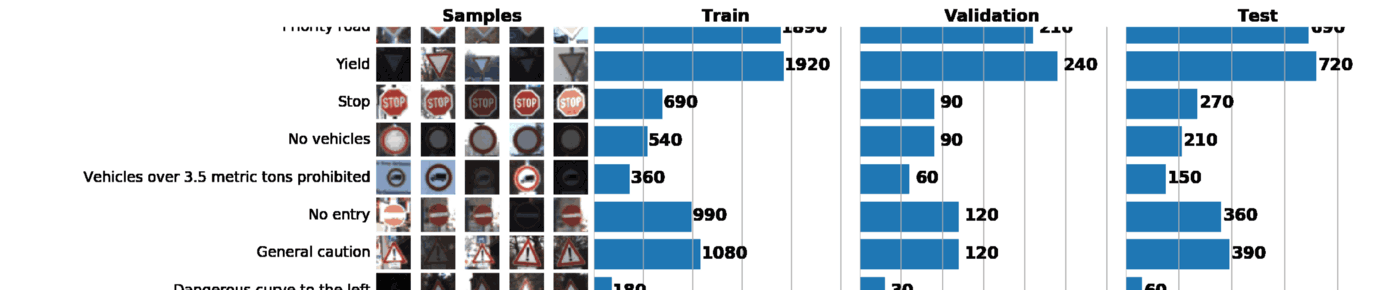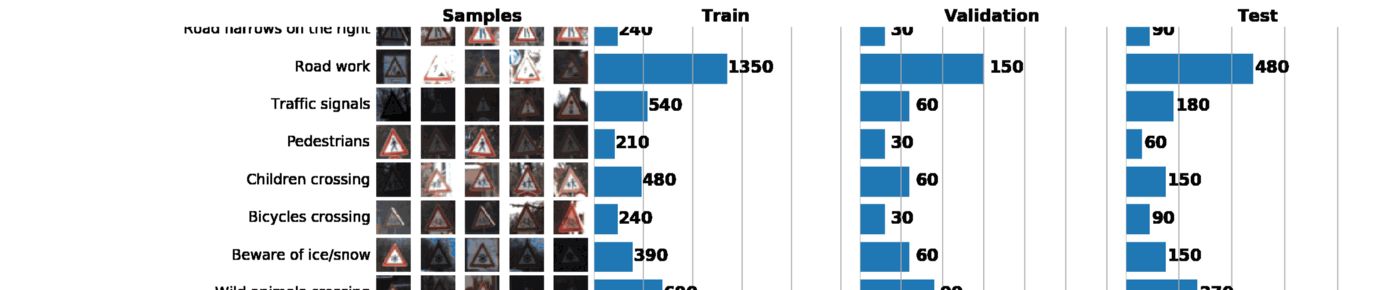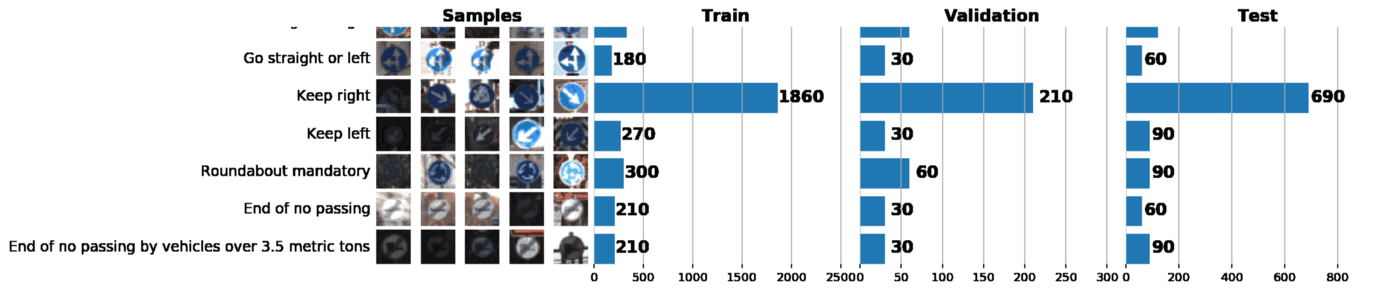
Ѕазова€ информаци€ о нашем датасете:
Ќа данном этапе
¬ результате всего один график может сказать о нашем наборе данных очень многое. Ќиже указаны 3 задачи, которые можно решить с помощью грамотно построенного графика:
ƒл€ того, чтобы улучшить сходимость нейронной сети, нужно привести все изображени€ к единому освещению путем (как рекомендовано в статье LeCun о распознавании дорожных знаков) преобразовани€ их цветовой гаммы в градации серого. Ёто можно сделать как с помощью OpenCV, так и с помощью отличной библиотеки на Python
ќтмечу, что
Ќаш подход к распараллеливанию очень прост: мы раздел€ем выборку на батчи и обрабатываем каждую партию независимо от остальных. ак только все батчи будут обработаны, мы сливаем их обратно в один набор данных. ћо€ реализаци€ CLAHE приведена ниже:
“еперь, когда сама трансформаци€ готова, напишем код, который примен€ет ее к каждому батчу из обучающей выборки:
Ќаконец, применим написанную функцию к обучающей выборке:
¬ результате мы используем не одно, а все €дра процессора (32 в моем случае) и получаем значительное увеличение производительности. ѕример полученных изображений:

–езультат нормализации изображений и переноса их цветовой гаммы в градации серого

Ќормализаци€ распределени€ дл€ изображений формата RGB (€ использовал другую функцию дл€ rc[:].map)
“еперь весь процесс предобработки данных проходит за несколько дес€тков секунд, поэтому мы можем протестировать разные значени€ числа интервалов

num_bins: 8, 32, 128, 256, 512
¬ыбор большего числа
Ќаконец, используем ipython magic
Ќи дл€ кого не секрет, что добавление новых разнообразных данных в выборку снижает веро€тность переобучени€ нейронной сети. ¬ нашем случае мы можем сконструировать искусственные изображени€ путем трансформации имеющихс€ картинок c помощью вращени€, зеркального отражени€ и аффиных преобразований. Ќесмотр€ на то, что мы можем провести данный процесс дл€ всей выборки, сохранить результаты и затем использовать их же, более элегантным способом будет создавать новые изображени€ Ђна летуї (онлайн), чтобы можно было оперативно корректировать параметры аугментации данных.
ƒл€ начала обозначим все планируемые преобразовани€, использу€
ћасштабирование и рандомные повороты
„асть таблицы преобразований. «начени€ в €чейках показывают номер класса, который примет данное изображение после трансформации. ѕустые €чейки означают, что данное преобразование недоступно дл€ этого класса.
ќбратите внимание, что заголовки столбцов соответствуют названи€м трансформирующих функций, определенных ранее, чтобы по ходу обработки можно было добавл€ть преобразовани€:
“еперь мы можем построить пайплайн, который примен€ет все доступные функции (преобразовани€), перечисленные в
ќтлично! “еперь у нас есть 2 готовые функции аугментации данных:
‘инальный шаг Ч это создать генератор батчей:
ќбъединив датасеты с разным числом
—генерированные с помощью augmented_batch_generator изображени€
«амечание: аугментаци€ нужна дл€ train-сета. Test-сет мы тоже предобрабатываем, но не аугментируем.
ƒавайте проверим, что мы неча€нно не нарушили распределение классов на расширенном трейне по сравнению с исходным датасетом:
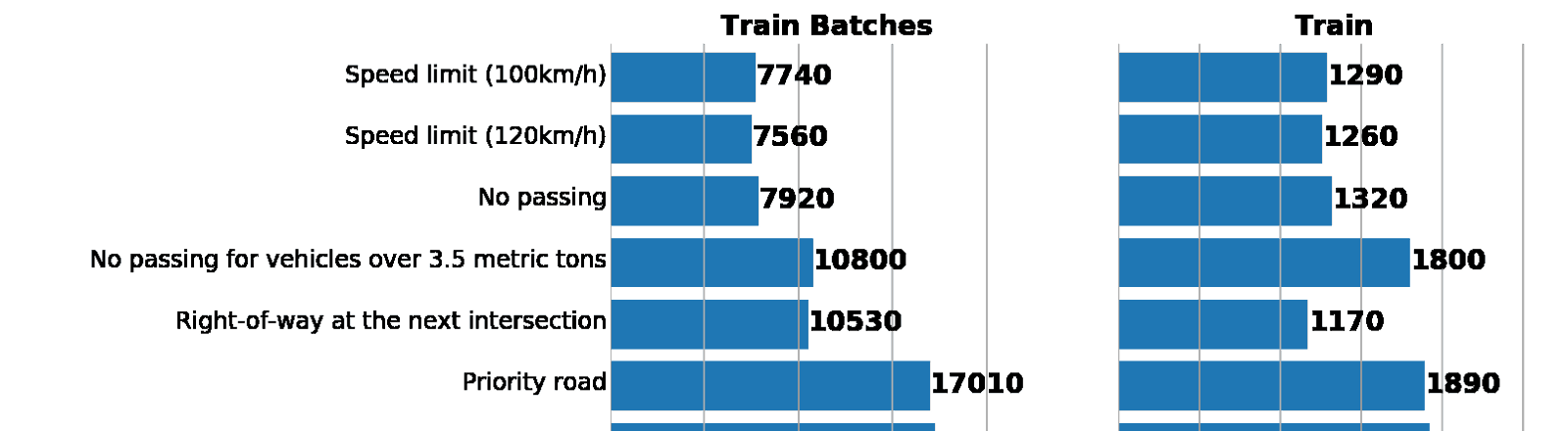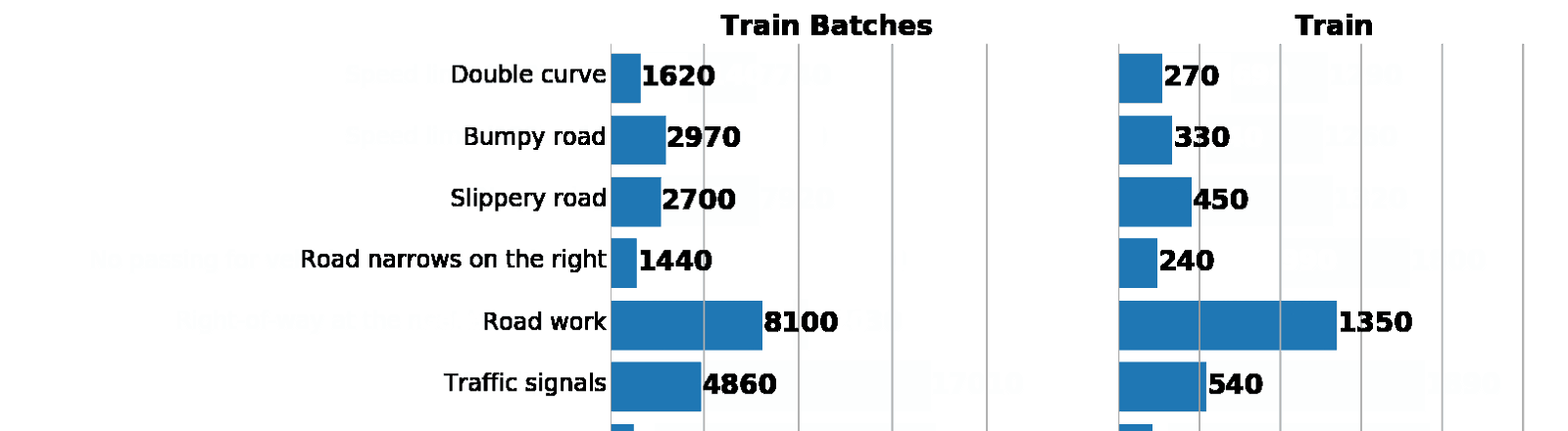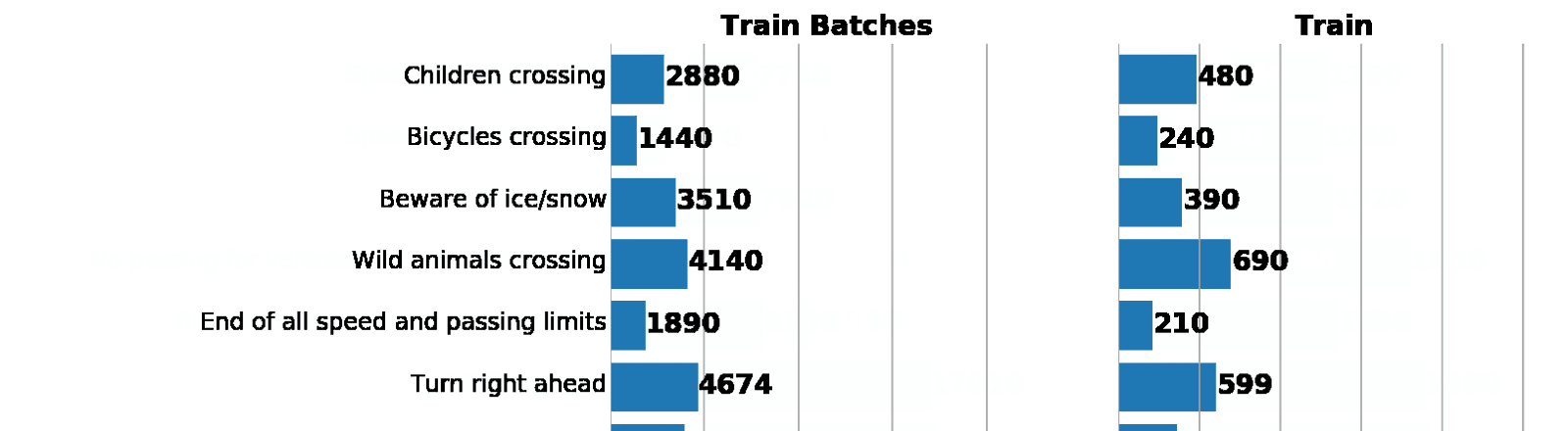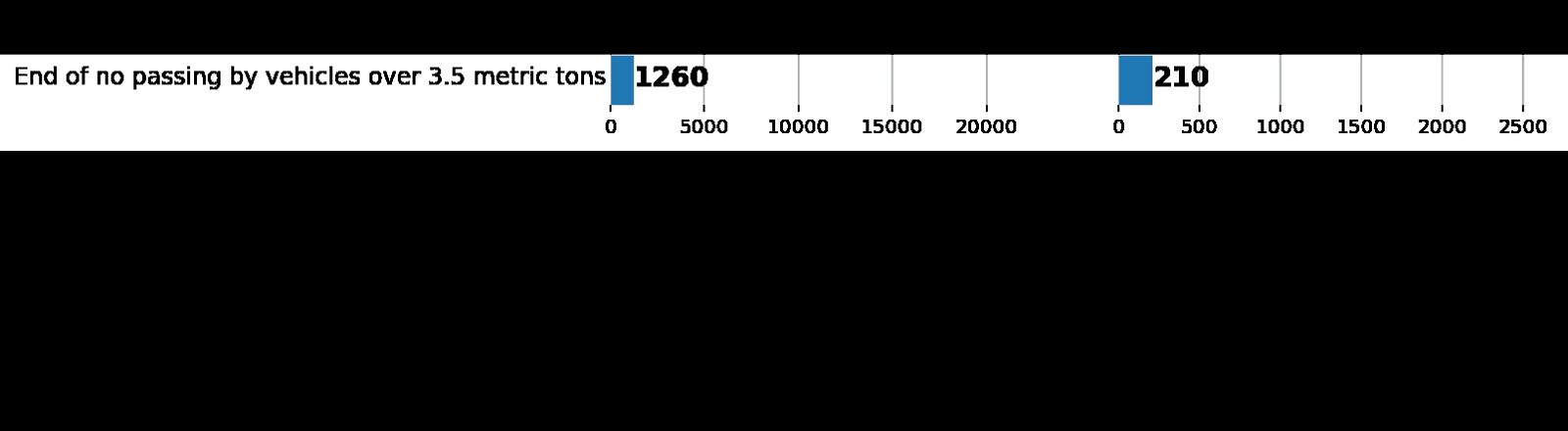
—лева: гистограмма распределени€ данных из augmented batch generator. —права: изначальный train. ак видно, значени€ различаютс€, но распределени€ схожи.
ѕосле того, как выполнена предобработка данных, все генераторы готовы и датасет готов к анализу, мы можем перейти к обучению. ћы будем использовать двойную свЄрточную нейронную сеть: STN (spatial transformer network) принимает на вход предобработанные батчи изображений из генератора и фокусируетс€ на дорожных знаках, а IDSIA нейросеть распознает дорожный знак на изображени€х, полученных от STN. —ледующий пост будет посв€щЄн этим нейросет€м, их обучению, анализу качества и демо-версии их работы. —ледите за новыми постами!
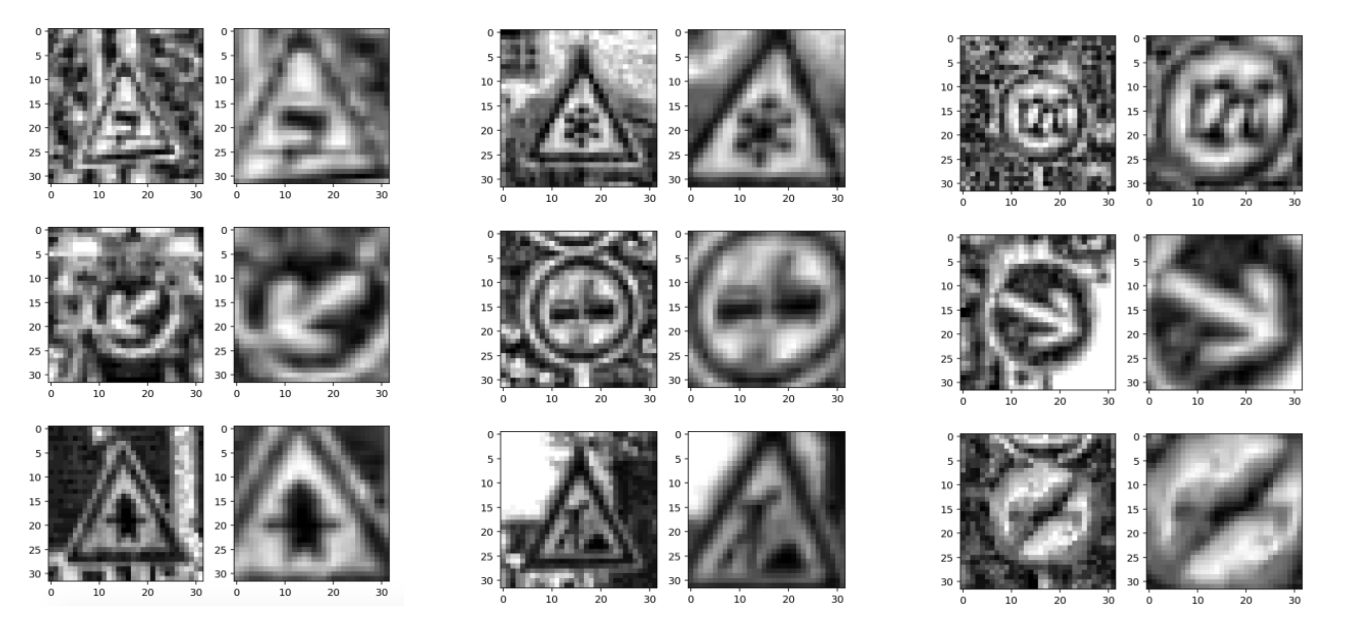
—лева: исходное предобработанное изображение. —права: преобразованное STN изображение, которое принимает на вход IDSIA дл€ классификации.
ћетки:
author a-pichugin
обработка изображений
data mining
big data
блог компании new professions lab
распознавание изображений
data augmentation
предобработка данных
¬ведение
«а последние несколько лет сфера компьютерного зрени€ (CV) переживает если не второе рождение, то огромный всплеск интереса к себе. ¬о многом такой рост попул€рности св€зан с эволюцией нейросетевых технологий. Ќапример, сверточные нейронные сети (convolutional neural networks или CNN) отобрали себе большой кусок задач по генерации фич, ранее решаемых классическими методиками CV: HOG, SIFT, RANSAC и т.д.
ћаппинг, классификаци€ изображений, построение маршрута дл€ дронов и беспилотных автомобилей Ч множество задач, св€занных с генерацией фич, классификацией, сегментацией изображений могут быть эффективно решены с помощью сверточных нейронных сетей.

MultiNet как пример нейронной сети (трех в одной), которую мы будем использовать в одном из следующих постов. »сточник.
ѕредполагаетс€, что читатель имеет общее представление о работе нейронных сетей. ¬ сети есть огромное количество постов, курсов и книг на данную тему. примеру:
- Chapter 6: Deep Feedforward Networks Ч глава из книги Deep Learning от I.Goodfellow, Y.Bengio и A.Courville. ќчень рекомендую.
- CS231n Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition Ч попул€рный курс от Fei-Fei Li и Andrej Karpathy из —тэнфорда. ¬ курсе содержатс€ отличные материалы сделан упор на практику и проектирование.
- Deep Learning Ч курс от Nando de Freitas из ќксфорда.
- Intro to Machine Learning Ч бесплатный курс от Udacity дл€ новичков с доступным изложением материала, затрагивает большое количество тем в машинном обучении.
—овет: чтобы убедитьс€ в том, что вы владеете основами нейронных сетей, напишите свою сеть с нул€ и поиграйте с ней!
¬место того, чтобы повтор€ть основы, данна€ сери€ статей фокусируетс€ на нескольких конкретных архитектурах нейронных сетей: STN (spatial transformer network), IDSIA (сверточна€ нейросеть дл€ классификации дорожных знаков), нейросеть от NVIDIA дл€ end-to-end разработки автопилота и MultiNet дл€ распознавани€ и классификации дорожной разметки и знаков. ѕриступим!
“ема данной статьи Ч показать несколько инструментов дл€ предобработки изображений. ќбщий пайплайн обычно зависит от конкретной задачи, € же хотел бы остановитьс€ именно на инструментах. Ќейросети Ч совсем не те магические черные €щики, какими их люб€т преподносить в медиа: нельз€ просто вз€ть и Ђзакинутьї данных в сетку и ждать волшебных результатов. ѕо правилу shit in Ч shit out в лучшем случае, вы получите score хуже на несколько пунктов. ј, скорее всего, просто не сможете обучить сеть и никакие модные техники типа нормализации батчей или dropout вам не помогут. “аким образом, работу нужно начинать именно с данных: их чистки, нормализации и нормировки. ƒополнительно стоит задуматьс€ над расширением (data augmentation) исходного картиночного датасета с помощью аффинных преобразований типа вращени€, сдвигов, изменени€ масштаба картинок: это поможет снизить веро€тность переобучени€ и обеспечит лучшую инвариантность классификатора к трансформаци€м.
»нструмент 1: ¬изуализаци€ и разведочный анализ данных
¬ рамках этого и следующего постов мы будем использовать GTSRB Ч датасет по распознаванию дорожных знаков в √ермании. Ќаша задача Ч обучить классификатор дорожных знаков, использу€ размеченные данные из GTSRB. ¬ общем случае, лучший способ получить представление об имеющихс€ данных Ч построить гистограмму распределени€ train, validation и/или test наборов данных:

Ѕазова€ информаци€ о нашем датасете:
Number of training examples = 34799
Number of validation examples = 4410
Number of testing examples = 12630
Image data shape = (32, 32, 3)
Number of classes = 43Ќа данном этапе
matplotlib Ч ваш лучший друг. Ќесмотр€ на то, что использу€ лишь pyplot можно отлично визуализировать данные, matplotlib.gridspec позвол€ет слить 3 графика воедино:gs = gridspec.GridSpec(1, 3, wspace=0.25, hspace=0.1)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,2))
ax1, ax2, ax3 = [plt.subplot(gs[:, i]) for i in range(3)]Gridspec очень гибок. примеру, дл€ каждой гистограммы можно установить свою ширину, как € это сделал выше. Gridspec рассматривает ось каждой гистограммы независимо от других, что позвол€ет создавать усложненные графики.
¬ результате всего один график может сказать о нашем наборе данных очень многое. Ќиже указаны 3 задачи, которые можно решить с помощью грамотно построенного графика:
- ¬изуализаци€ изображений. ѕо графику сразу видно множество слишком темных или слишком светлых изображений, поэтому должна быть проведена своего рода нормализаци€ данных, чтобы устранить вариацию €ркости.
- ѕроверка выборки на несбалансированность. ¬ случае, если в выборке превалируют экземпл€ры какого-либо класса, необходимо использовать методы undersampling или oversampling.
- ѕроверить, что распределени€ train, validation и test выборок похожи. Ёто можно проверить, взгл€нув на гистограммы выше, либо использу€ ранговый коэффициент коррел€ции —пирмена. (через
scipy)
»нструмент 2: IPython Parallel дл€ scikit-image
ƒл€ того, чтобы улучшить сходимость нейронной сети, нужно привести все изображени€ к единому освещению путем (как рекомендовано в статье LeCun о распознавании дорожных знаков) преобразовани€ их цветовой гаммы в градации серого. Ёто можно сделать как с помощью OpenCV, так и с помощью отличной библиотеки на Python
scikit-image, котора€ может быть легко установлена с помощью pip (OpenCV же требует самосто€тельной компил€ции с кучей зависимостей). Ќормализаци€ контрастности изображений будет осуществл€тьс€ с помощью адаптивной нормализации гистограммы (CLAHE, contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization):skimage.exposure.equalize_adapthist.ќтмечу, что
skimage обрабатывает изображени€ одно за другим, использу€ лишь одно €дро процессора, что, очевидно, неэффективно. „тобы распараллелить предобработку изображений, используем библиотеку IPython Parallel (ipyparallel). ќдно из преимуществ этой библиотеки Ч простота: реализовать распараллеленный CLAHE можно всего несколькими строчками кода. —начала в консоли (с установленной ipyparallel) запустим локальный кластер ipyparallel:$ ipcluster start
Ќаш подход к распараллеливанию очень прост: мы раздел€ем выборку на батчи и обрабатываем каждую партию независимо от остальных. ак только все батчи будут обработаны, мы сливаем их обратно в один набор данных. ћо€ реализаци€ CLAHE приведена ниже:
from skimage import exposure
def grayscale_exposure_equalize(batch_x_y):
"""Processes a batch with images by grayscaling, normalization and
histogram equalization.
Args:
batch_x_y: a single batch of data containing a numpy array of images
and a list of corresponding labels.
Returns:
Numpy array of processed images and a list of labels (unchanged).
"""
x_sub, y_sub = batch_x_y[0], batch_x_y[1]
x_processed_sub = numpy.zeros(x_sub.shape[:-1])
for x in range(len(x_sub)):
# Grayscale
img_gray = numpy.dot(x_sub[x][...,:3], [0.299, 0.587, 0.114])
# Normalization
img_gray_norm = img_gray / (img_gray.max() + 1)
# CLAHE. num_bins will be initialized in ipyparallel client
img_gray_norm = exposure.equalize_adapthist(img_gray_norm, nbins=num_bins)
x_processed_sub[x,...] = img_gray_norm
return (x_processed_sub, y_sub)“еперь, когда сама трансформаци€ готова, напишем код, который примен€ет ее к каждому батчу из обучающей выборки:
import multiprocessing
import ipyparallel as ipp
import numpy as np
def preprocess_equalize(X, y, bins=256, cpu=multiprocessing.cpu_count()):
""" A simplified version of a function which manages multiprocessing logic.
This function always grayscales input images, though it can be generalized
to apply any arbitrary function to batches.
Args:
X: numpy array of all images in dataset.
y: a list of corresponding labels.
bins: the amount of bins to be used in histogram equalization.
cpu: the number of cpu cores to use. Default: use all.
Returns:
Numpy array of processed images and a list of labels.
"""
rc = ipp.Client()
# Use a DirectView object to broadcast imports to all engines
with rc[:].sync_imports():
import numpy
from skimage import exposure, transform, color
# Use a DirectView object to set up the amount of bins on all engines
rc[:]['num_bins'] = bins
X_processed = np.zeros(X.shape[:-1])
y_processed = np.zeros(y.shape)
# Number of batches is equal to cpu count
batches_x = np.array_split(X, cpu)
batches_y = np.array_split(y, cpu)
batches_x_y = zip(batches_x, batches_y)
# Applying our function of choice to each batch with a DirectView method
preprocessed_subs = rc[:].map(grayscale_exposure_equalize, batches_x_y).get_dict()
# Combining the output batches into a single dataset
cnt = 0
for _,v in preprocessed_subs.items():
x_, y_ = v[0], v[1]
X_processed[cnt:cnt+len(x_)] = x_
y_processed[cnt:cnt+len(y_)] = y_
cnt += len(x_)
return X_processed.reshape(X_processed.shape + (1,)), y_processedЌаконец, применим написанную функцию к обучающей выборке:
# X_train: numpy array of (34799, 32, 32, 3) shape
# y_train: a list of (34799,) shape
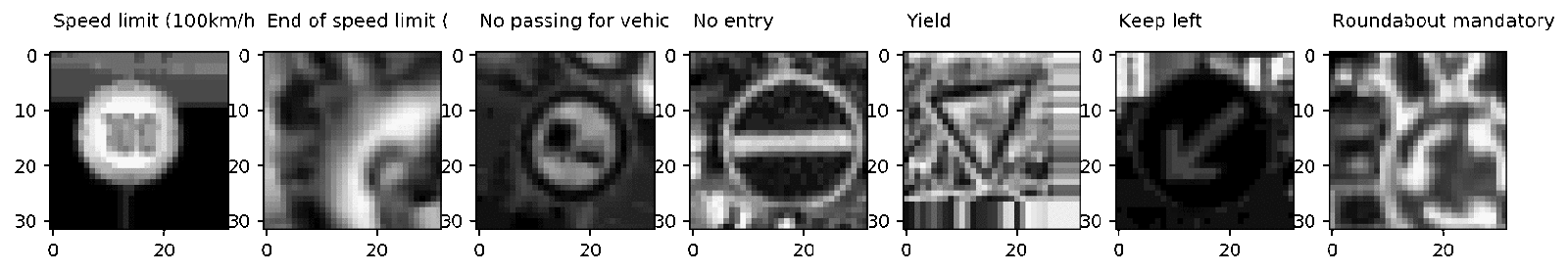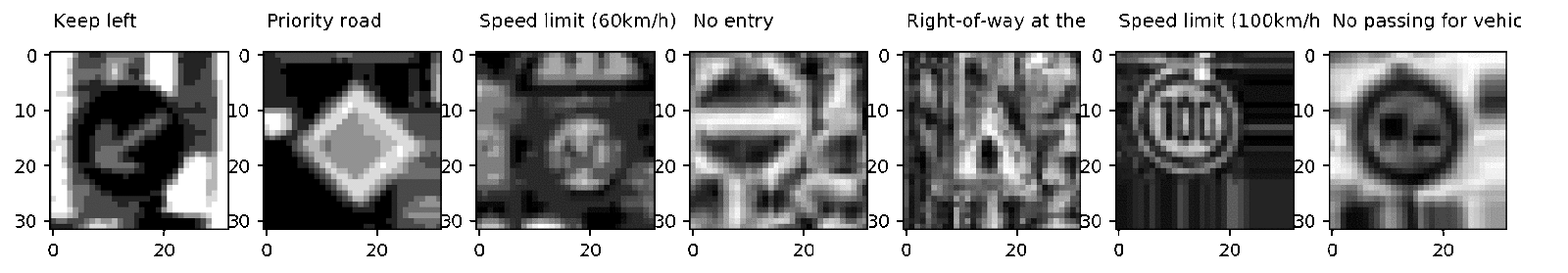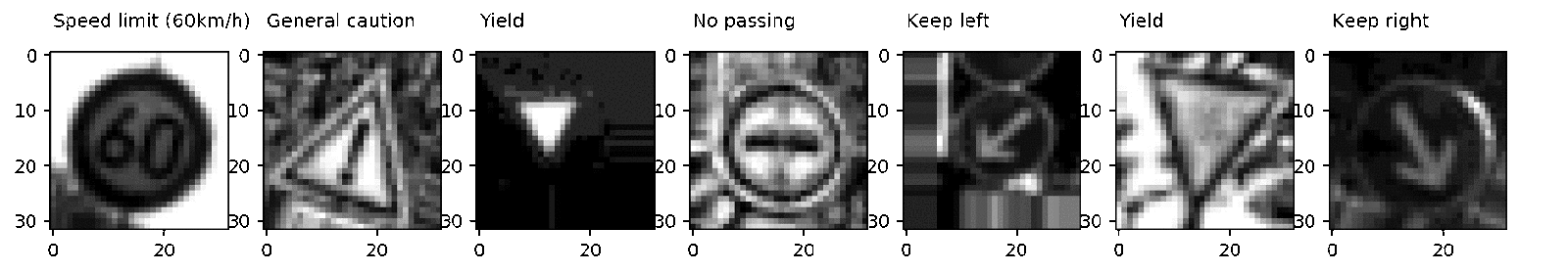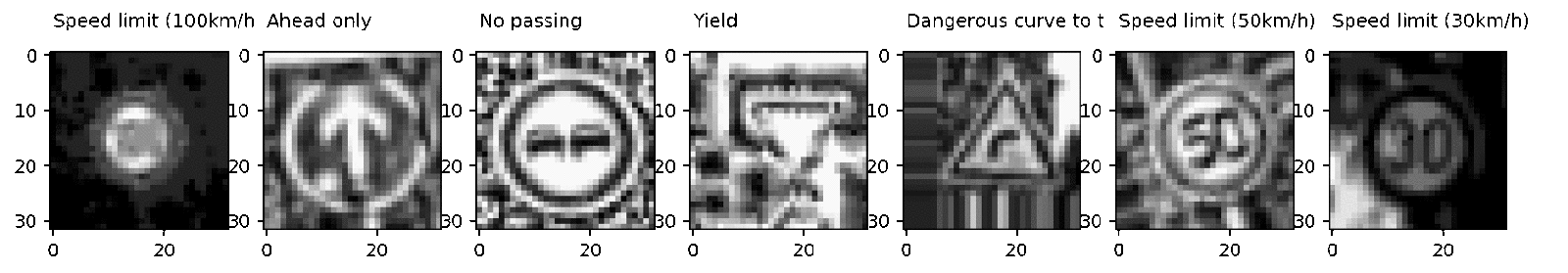
X_tr, y_tr = preprocess_equalize(X_train, y_train, bins=128)¬ результате мы используем не одно, а все €дра процессора (32 в моем случае) и получаем значительное увеличение производительности. ѕример полученных изображений:

–езультат нормализации изображений и переноса их цветовой гаммы в градации серого

Ќормализаци€ распределени€ дл€ изображений формата RGB (€ использовал другую функцию дл€ rc[:].map)
“еперь весь процесс предобработки данных проходит за несколько дес€тков секунд, поэтому мы можем протестировать разные значени€ числа интервалов
num_bins, чтобы визуализировать их и выбрать наиболее подход€щий:
num_bins: 8, 32, 128, 256, 512
¬ыбор большего числа
num_bins увеличивает контрастность изображений, в то же врем€ сильно выдел€€ их фон, что зашумл€ет данные. –азные значени€ num_bins также могут быть использованы дл€ аугментации контрастности датасета путем контраста дл€ того, чтобы нейросеть не переобучалась из-за фона изображений.Ќаконец, используем ipython magic
%store, чтобы сохранить результаты дл€ дальнейшего использовани€:# Same images, multiple bins (contrast augmentation)
%store X_tr_8
%store y_tr_8
# ...
%store X_tr_512
%store y_tr_512»нструмент 3: ќнлайн-аугментаци€ данных
Ќи дл€ кого не секрет, что добавление новых разнообразных данных в выборку снижает веро€тность переобучени€ нейронной сети. ¬ нашем случае мы можем сконструировать искусственные изображени€ путем трансформации имеющихс€ картинок c помощью вращени€, зеркального отражени€ и аффиных преобразований. Ќесмотр€ на то, что мы можем провести данный процесс дл€ всей выборки, сохранить результаты и затем использовать их же, более элегантным способом будет создавать новые изображени€ Ђна летуї (онлайн), чтобы можно было оперативно корректировать параметры аугментации данных.
ƒл€ начала обозначим все планируемые преобразовани€, использу€
numpy и skimage:import numpy as np
from skimage import transform
from skimage.transform import warp, AffineTransform
def rotate_90_deg(X):
X_aug = np.zeros_like(X)
for i,img in enumerate(X):
X_aug[i] = transform.rotate(img, 270.0)
return X_aug
def rotate_180_deg(X):
X_aug = np.zeros_like(X)
for i,img in enumerate(X):
X_aug[i] = transform.rotate(img, 180.0)
return X_aug
def rotate_270_deg(X):
X_aug = np.zeros_like(X)
for i,img in enumerate(X):
X_aug[i] = transform.rotate(img, 90.0)
return X_aug
def rotate_up_to_20_deg(X):
X_aug = np.zeros_like(X)
delta = 20.
for i,img in enumerate(X):
X_aug[i] = transform.rotate(img, random.uniform(-delta, delta), mode='edge')
return X_aug
def flip_vert(X):
X_aug = deepcopy(X)
return X_aug[:, :, ::-1, :]
def flip_horiz(X):
X_aug = deepcopy(X)
return X_aug[:, ::-1, :, :]
def affine_transform(X, shear_angle=0.0, scale_margins=[0.8, 1.5], p=1.0):
"""This function allows applying shear and scale transformations
with the specified magnitude and probability p.
Args:
X: numpy array of images.
shear_angle: maximum shear angle in counter-clockwise direction as radians.
scale_margins: minimum and maximum margins to be used in scaling.
p: a fraction of images to be augmented.
"""
X_aug = deepcopy(X)
shear = shear_angle * np.random.rand()
for i in np.random.choice(len(X_aug), int(len(X_aug) * p), replace=False):
_scale = random.uniform(scale_margins[0], scale_margins[1])
X_aug[i] = warp(X_aug[i], AffineTransform(scale=(_scale, _scale), shear=shear), mode='edge')
return X_augћасштабирование и рандомные повороты
rotate_up_to_20_deg увеличивают размер выборки, сохран€€ принадлежность изображений к исходным классам. ќтражени€ (flips) и вращени€ на 90, 180, 270 градусов могут, напротив, помен€ть смысл знака. „тобы отслеживать такие переходы, создадим список возможных преобразований дл€ каждого дорожного знака и классов, в которые они будут преобразованы (ниже приведен пример части такого списка):| label_class | label_name | rotate_90_deg | rotate_180_deg | rotate_270_deg | flip_horiz | flip_vert |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | Yield | 13 | ||||
| 14 | Stop | |||||
| 15 | No vehicles | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| 16 | Vehicles over 3.5 ton prohibited |
|||||
| 17 | No entry | 17 | 17 | 17 |
ќбратите внимание, что заголовки столбцов соответствуют названи€м трансформирующих функций, определенных ранее, чтобы по ходу обработки можно было добавл€ть преобразовани€:
import pandas as pd
# Generate an augmented dataset using a transform table
augmentation_table = pd.read_csv('augmentation_table.csv', index_col='label_class')
augmentation_table.drop('label_name', axis=1, inplace=True)
augmentation_table.dropna(axis=0, how='all', inplace=True)
# Collect all global functions in global namespace
namespace = __import__(__name__)
def apply_augmentation(X, how=None):
"""Apply an augmentation function specified in `how` (string) to a numpy array X.
Args:
X: numpy array with images.
how: a string with a function name to be applied to X, should return
the same-shaped numpy array as in X.
Returns:
Augmented X dataset.
"""
assert augmentation_table.get(how) is not None
augmentator = getattr(namespace, how)
return augmentator(X)“еперь мы можем построить пайплайн, который примен€ет все доступные функции (преобразовани€), перечисленные в
augmentation_table.csv ко всем классам:import numpy as np
def flips_rotations_augmentation(X, y):
"""A pipeline for applying augmentation functions listed in `augmentation_table`
to a numpy array with images X.
"""
# Initializing empty arrays to accumulate intermediate results of augmentation
X_out, y_out = np.empty([0] + list(X.shape[1:]), dtype=np.float32), np.empty([0])
# Cycling through all label classes and applying all available transformations
for in_label in augmentation_table.index.values:
available_augmentations = dict(augmentation_table.ix[in_label].dropna(axis=0))
images = X[y==in_label]
# Augment images and their labels
for kind, out_label in available_augmentations.items():
X_out = np.vstack([X_out, apply_augmentation(images, how=kind)])
y_out = np.hstack([y_out, [out_label] * len(images)])
# And stack with initial dataset
X_out = np.vstack([X_out, X])
y_out = np.hstack([y_out, y])
# Random rotation is explicitly included in this function's body
X_out_rotated = rotate_up_to_20_deg(X)
y_out_rotated = deepcopy(y)
X_out = np.vstack([X_out, X_out_rotated])
y_out = np.hstack([y_out, y_out_rotated])
return X_out, y_outќтлично! “еперь у нас есть 2 готовые функции аугментации данных:
affine_transform: кастомизируемые аффинные преобразовани€ без вращени€ (название € выбрал не очень удачное, потому что, что вращение €вл€етс€ одним из аффинных преобразований).flips_rotations_augmentation: случайные вращени€ и преобразовани€ на основеaugmentation_table.csv, мен€ющие классы изображений.
‘инальный шаг Ч это создать генератор батчей:
def augmented_batch_generator(X, y, batch_size, rotations=True, affine=True,
shear_angle=0.0, scale_margins=[0.8, 1.5], p=0.35):
"""Augmented batch generator. Splits the dataset into batches and augments each
batch independently.
Args:
X: numpy array with images.
y: list of labels.
batch_size: the size of the output batch.
rotations: whether to apply `flips_rotations_augmentation` function to dataset.
affine: whether to apply `affine_transform` function to dataset.
shear_angle: `shear_angle` argument for `affine_transform` function.
scale_margins: `scale_margins` argument for `affine_transform` function.
p: `p` argument for `affine_transform` function.
"""
X_aug, y_aug = shuffle(X, y)
# Batch generation
for offset in range(0, X_aug.shape[0], batch_size):
end = offset + batch_size
batch_x, batch_y = X_aug[offset:end,...], y_aug[offset:end]
# Batch augmentation
if affine is True:
batch_x = affine_transform(batch_x, shear_angle=shear_angle, scale_margins=scale_margins, p=p)
if rotations is True:
batch_x, batch_y = flips_rotations_augmentation(batch_x, batch_y)
yield batch_x, batch_yќбъединив датасеты с разным числом
num_bins в CLAHE в один большой train, подадим его в полученный генератор. “еперь у нас есть два вида аугментации: по контрастности и с помощью аффинных трансформаций, которые примен€ютс€ к батчу на лету:
—генерированные с помощью augmented_batch_generator изображени€
«амечание: аугментаци€ нужна дл€ train-сета. Test-сет мы тоже предобрабатываем, но не аугментируем.
ƒавайте проверим, что мы неча€нно не нарушили распределение классов на расширенном трейне по сравнению с исходным датасетом:

—лева: гистограмма распределени€ данных из augmented batch generator. —права: изначальный train. ак видно, значени€ различаютс€, но распределени€ схожи.
ѕереход к нейронным сет€м
ѕосле того, как выполнена предобработка данных, все генераторы готовы и датасет готов к анализу, мы можем перейти к обучению. ћы будем использовать двойную свЄрточную нейронную сеть: STN (spatial transformer network) принимает на вход предобработанные батчи изображений из генератора и фокусируетс€ на дорожных знаках, а IDSIA нейросеть распознает дорожный знак на изображени€х, полученных от STN. —ледующий пост будет посв€щЄн этим нейросет€м, их обучению, анализу качества и демо-версии их работы. —ледите за новыми постами!

—лева: исходное предобработанное изображение. —права: преобразованное STN изображение, которое принимает на вход IDSIA дл€ классификации.
| омментировать | « ѕред. запись — дневнику — —лед. запись » | —траницы: [1] [Ќовые] |






