Hacks.Mozilla.Org: Teaching machines to triage Firefox bugs |
Many bugs, not enough triage
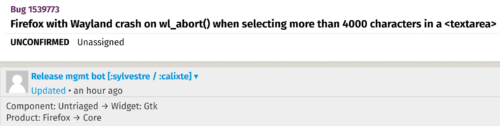
Mozilla receives hundreds of bug reports and feature requests from Firefox users every day. Getting bugs to the right eyes as soon as possible is essential in order to fix them quickly. This is where bug triage comes in: until a developer knows a bug exists, they won’t be able to fix it.
Given the large number of bugs filed, it is unworkable to make each developer look at every bug (at the time of writing, we’d reached bug number 1536796!). This is why, on Bugzilla, we group bugs by product (e.g. Firefox, Firefox for Android, Thunderbird, etc.) and component (a subset of a product, e.g. Firefox::PDF Viewer).
Historically, the product/component assignment has been mostly done manually by volunteers and some developers. Unfortunately, this process fails to scale, and it is effort that would be better spent elsewhere.
Introducing BugBug
To help get bugs in front of the right Firefox engineers quickly, we developed BugBug, a machine learning tool that automatically assigns a product and component for each new untriaged bug. By presenting new bugs quickly to triage owners, we hope to decrease the turnaround time to fix new issues. The tool is based on another technique that we have implemented recently, to differentiate between bug reports and feature requests. (You can read more about this at https://marco-c.github.io/2019/01/18/bugbug.html).
Training a model
We have a large training set of data for this model: two decades worth of bugs which have been reviewed by Mozillians and assigned to products and components.
Clearly we can’t use the bug data as-is: any change to the bug after triage has been completed would be inaccessible to the tool during real operation. So, we “roll back” the bug to the time it was originally filed. (This sounds easy in practice, but there are a lot of corner cases to take into account!).
Also, although we have thousands of components, we only really care about a subset of these. In the past ~2 years, out of 396 components, only 225 components had more than 49 bugs filed. Thus, we restrict the tool to only look at components with a number of bugs that is at least 1% of the number of bugs of the largest component.
We use features collected from the title, the first comment, and the keywords/flags associated with each bug to train an XGBoost model.
During operation, we only perform the assignment when the model is confident enough of its decision: at the moment, we are using a 60% confidence threshold. With this threshold, we are able to assign the right component with a very low false positive ratio (> 80% precision, measured using a validation set of bugs that were triaged between December 2018 and March 2019).
BugBug’s results
Training the model on 2+ years of data (around 100,000 bugs) takes ~40 minutes on a 6-core machine with 32 GB of RAM. The evaluation time is in the order of milliseconds. Given that the tool does not pause and is always ready to act, the tool’s assignment speed is much faster than manual assignment (which, on average, takes around a week).
Since we deployed BugBug in production at the end of February 2019, we’ve triaged around 350 bugs. The median time for a developer to act on triaged bugs is 2 days. (9 days is the average time to act, but it’s only 4 days when we remove outliers.)
Plans for the future
We have plans to use machine learning to assist in other software development processes, for example:
- Identifying duplicate bugs. In the case of bugs which crash Firefox, users will typically report the same bug several times, in slightly different ways. These duplicates are eventually found by the triage process, and resolved, but finding duplicate bugs as quickly as possible provides more information for developers trying to diagnose a crash.
- Providing additional automated help for developers, such as detecting bugs in which “steps to reproduce” are missing and asking reporters to provide them, or detecting the type of bug (e.g. performance, memory usage, crash, and so on).
- Detecting bugs that might be important for a given Firefox release as early as possible.
Right now our tool only assigns components for Firefox-related products. We would like to extend BugBug to automatically assign components for other Mozilla products.
We also encourage other organizations to adopt BugBug. If you use Bugzilla, adopting it will be very easy; otherwise, we’ll need to add support for your bug tracking system. File an issue on https://github.com/mozilla/bugbug and we’ll figure it out. We are willing to help!
The post Teaching machines to triage Firefox bugs appeared first on Mozilla Hacks - the Web developer blog.
https://hacks.mozilla.org/2019/04/teaching-machines-to-triage-firefox-bugs/
| Комментировать | « Пред. запись — К дневнику — След. запись » | Страницы: [1] [Новые] |