Tanvi Vyas: No More Passwords over HTTP, Please! |
Firefox Developer Edition 46 warns developers when login credentials are requested over HTTP.
Username and password pairs control access to users’ personal data. Websites should handle this information with care and only request passwords over secure (authenticated and encrypted) connections, like HTTPS. Unfortunately, we too frequently see non-secure connections, like HTTP, used to handle user passwords. To inform developers about this privacy and security vulnerability, Firefox Developer Edition warns developers of the issue by changing the security iconography of non-secure pages to a lock with a red strikethrough.
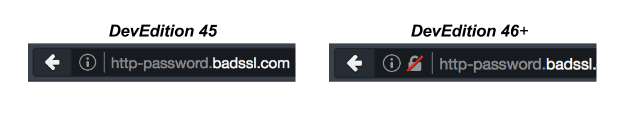
How does Firefox determine if a password field is secure or not?
Firefox determines if a password field is secure by examining the page it is embedded in. The embedding page is checked against the algorithm in the W3C’s Secure Contexts Specification to see if it is secure or non-secure. Anything on a non-secure page can be manipulated by a Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attacker. The MITM can use a number of mechanisms to extract the password entered onto the non-secure page. Here are some examples:
- Change the form action so the password submits to an attacker controlled server instead of the intended destination. Then seamlessly redirect to the intended destination, while sending along the stolen password.
- Use javascript to grab the contents of the password field before submission and send it to the attacker’s server.
- Use javascript to log the user’s keystrokes and send them to the attacker’s server.
Note that all of the attacks mentioned above can occur without the user realizing that their account has been compromised.
Firefox has been alerting developers of this issue via the Developer Tools Web Console since Firefox 26.
Why isn’t submitting over HTTPS enough? Why does the page have to be HTTPS?
We get this question a lot, so I thought I would call it out specifically. Although transmitting over HTTPS instead of HTTP does prevent a network eavesdropper from seeing a user’s password, it does not prevent an active MITM attacker from extracting the password from the non-secure HTTP page. As described above, active attackers can MITM an HTTP connection between the server and the user’s computer to change the contents of the webpage. The attacker can take the HTML content that the site attempted to deliver to the user and add javascript to the HTML page that will steal the user’s username and password. The attacker then sends the updated HTML to the user. When the user enters their username and password, it will get sent to both the attacker and the site.
What if the credentials for my site really aren’t that sensitive?
Sometimes sites require username and passwords, but don’t actually store data that is very sensitive. For example, a news site may save which news articles a user wants to go back and read, but not save any other data about a user. Most users don’t consider this highly sensitive information. Web developers of the news site may be less motivated to secure their site and their user credentials. Unfortunately, password reuse is a big problem. Users use the same password across multiple sites (news sites, social networks, email providers, banks). Hence, even if access to the username and password to your site doesn’t seem like a huge risk to you, it is a great risk to users who have used the same username and password to login to their bank accounts. Attackers are getting smarter; they steal username/password pairs from one site, and then try reusing them on more lucrative sites.
How can I remove this warning from my site?
Put your login forms on HTTPS pages.
Of course, the most straightforward way to do this is to move your whole website to HTTPS. If you aren’t able to do this today, create a separate HTTPS page that is just used for logins. Whenever a user wants to login to your site, they will visit the HTTPS login page. If your login form submits to an HTTPS endpoint, parts of your domain may already be set up to use HTTPS.
In order to host content over HTTPS, you need a TLS Certificate from a Certificate Authority. Let’s Encrypt is a Certificate Authority that can issue you free certificates. You can reference these pages for some guidance on configuring your servers.
What can I do if I don’t control the webpage?
We know that users of Firefox Developer Edition don’t only use Developer Edition to work on their own websites. They also use it to browse the net. Developers who see this warning on a page they don’t control can still take a couple of actions. You can try to add “https://” to the beginning of the url in the address bar and see if you are able to login over a secure connection to help protect your data. You can also try and reach out to the website administrator and alert them of the privacy and security vulnerability on their site.
Do you have examples of real life attacks that occurred because of stolen passwords?
There are ample examples of password reuse leading to large scale compromise. There are fewer well-known examples of passwords being stolen by performing MITM attacks on login forms, but the basic techniques of javascript injection have been used at scale by Internet Service Providers and governments.
Why does my browser sometimes show this warning when I don’t see a password field on the page?
Sometimes password fields are in a hidden
Will this feature become available to Firefox Beta and Release Users?
Right now, the focus for this feature is on developers, since they’re the ones that ultimately need to fix the sites that are exposing users’ passwords. In general, though, since we are working on deprecating non-secure HTTP in the long run, you should expect to see more and more explicit indications of when things are not secure. For example, in all current versions of Firefox, the Developer Tools Network Monitor shows the lock with a red strikethrough for all non-secure HTTP connections.
How do I enable this warning in other versions of Firefox?
Users of Firefox version 44+ (on any branch) can enable or disable this feature by following these steps:
- Open a new window or tab in Firefox.
- Type about:config and press enter.
- You will get to a page that asks you to promise to be careful. Promise you will be.
- The value of the security.insecure_password.ui.enabled preference determines whether or not Firefox warns you about non-secure login pages. You can enable the feature and be warned about non-secure login pages by setting this value to true. You can disable the feature by setting the value to false.
Thank you!
A special thanks to Paolo Amadini and Aislinn Grigas for their implementation and user experience work on this feature!
https://blog.mozilla.org/tanvi/2016/01/28/no-more-passwords-over-http-please/
| Комментировать | « Пред. запись — К дневнику — След. запись » | Страницы: [1] [Новые] |






