-Рубрики
- (6)
- (0)
- Alina Semukha is a mutual friend. (0)
- Arabic (16)
- Cilia Fur.Клетчанка. (1)
- DO YOU WANT TO BE A LONG LIFE? (50)
- Kharitonych (12)
- Деменция (7)
- English (58)
- Facebook.https: //www.facebook.com/eduard.furman. (1)
- Fighting insomnia .. (33)
- Food & Drinks (78)
- France (13)
- FURMAN_ED.ЗДОРОВЬЕ И КРАСОТА МУЖЧИНЫ (135)
- German (47)
- Google (3)
- Google Translate (83)
- Google.Откуда пошло выражение "нажить себе ге (8)
- Health & Lifestyle > Health (94)
- Health & Lifestyle > Health (1)
- Hebrew (10)
- Helena. Website NHEIT UND GESUNDHEIT. (49)
- Helena. Website NHEIT UND GESUNDHEIT. (22)
- Helena.DIÄTEN AUS ALLER WELT. (53)
- Helena.IMMER IN FORM! (41)
- Humor 84 (24)
- Israel Hayom Newsletter in English (1)
- komrik_valerya. (12)
- Memory, sight, hearing (9)
- Miroslava.USEFUL TIPS (28)
- My House (12)
- Panet.co.il (1) (0)
- Personal comments on my writings (152)
- Personal comments on my writings. (238)
- Personal University of Self-Development (266)
- Russian (43)
- Spam (5)
- Spanish (3)
- USA (14)
- Weight loss as part of health. (39)
- Welcome to Baba-Mail (1)
- Академик Бехтерев, (0)
- Ближний Восток.Израиль (5)
- Вайке. (11)
- Владимир Путин - лидер Великой Державы (19)
- Враги России. (6)
- Вторые блюда на каждый день: 20 рецептов вкусно, п (2)
- Гуакамоле - самое вкусное, что можно приготовить и (0)
- ДИЕТЫ СО ВСЕГО СВЕТА.Плюсы и минусы правильного пи (1)
- Другая Кухня.ЛЮБИМЫЕ РЕЦЕПТЫ.Слоеный яблочный руле (0)
- Имбирь (4)
- История (7)
- Каша овсяная. (0)
- Комсомольксая правда,21.11.2021.Все для одного Че (0)
- Комсомольская правда. Гречка: польза и вред для о (0)
- Кухня - это осталость нашего дома! (1)
- Кухня, где нам хорошо: просто, удобно и элегантно (0)
- Личная переписка... (55)
- Мировая война (4)
- Михаил Алексиев (11)
- Наука и техника (3)
- Наши издания — Российская газета (rg.ru) (1)
- Отдышка (17)
- ОТНОШЕНИЯ (2)
- Питание на одного Человека (0)
- Питье (1)
- Поварёнок.ру – главная страница Ежедневная рассылк (2)
- Русский язык для всех (137)
- Сахар (0)
- Среда обитания (4)
- Супы на каждый день. (3)
- Топ-10 интересных фактов про Оксфордский университ (0)
- Удивительное (3)
- Украинский (14)
- Учим немецкий по самоучителю (8) (7)
- Форум Метаргем 71-English,Hebrew,Arabic https (1)
- Черника (1)
- Чернослив (1)
- Чернослив (0)
- Что такое гастрит: симптомы и способы лечения (1)
-Поиск по дневнику
-Подписка по e-mail
-Постоянные читатели
-Статистика
Polyglot 84.195 Day of Life.From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.Arabic |
Arabic
| Arabic | |
|---|---|
|
اَلْعَرَبِيَّةُ al-ʿarabiyyah |
|

al-ʿarabiyyah in written Arabic (Naskh script)
|
|
| Pronunciation | /ˈʕarabiː/, /alʕaraˈbijːa/ |
| Native to | Countries of the Arab League, minorities in neighboring countries and some parts of Asia, Africa, Europe |
| Ethnicity | Arabs and the original peoples of the Middle East and North Africa (as a result of language shift) |
|
Native speakers
|
350 million, all varieties (2011–2020)[1] 270 million L2 speakers of Modern Standard Arabic[1] |
| Afro-Asiatic | |
|
Early form
|
Proto-Arabic Old Arabic Old Hijazi Classical Arabic |
|
Standard forms
|
|
| Dialects | |
|
Arabic alphabet Arabic Braille Arabizi |
|
| Signed Arabic (different national forms) | |
| Official status | |
|
Official language in
|
show
International Organizations
|
|
Recognised minority
language in |
show
List
|
| Regulated by |
show
List
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 |
ar |
| ISO 639-2 |
ara |
| ISO 639-3 |
ara – inclusive codeIndividual codes: arq – Algerian Arabicaao – Algerian Saharan Arabicxaa – Andalusian Arabicbbz – Babalia Creole Arabicabv – Baharna Arabicshu – Chadian Arabicacy – Cypriot Arabicadf – Dhofari Arabicavl – Eastern Egyptian Bedawi Arabicarz – Egyptian Arabicafb – Gulf Arabicayh – Hadrami Arabicacw – Hijazi Arabicayl – Libyan Arabicacm – Mesopotamian Arabicary – Moroccan Arabicars – Najdi Arabicapc – North Levantine Arabicayp – North Mesopotamian Arabicacx – Omani Arabicaec – Saidi Arabicayn – Sanaani Arabicssh – Shihhi Arabicsqr – Siculo Arabicajp – South Levantine Arabicarb – Standard Arabicapd – Sudanese Arabicpga – Sudanese Creole Arabicacq – Taizzi-Adeni Arabicabh – Tajiki Arabic |
| Glottolog |
arab1395 |
| Linguasphere |
12-AAC |

Dispersion of native Arabic speakers as the majority (dark green) or minority (light green) population
|
|
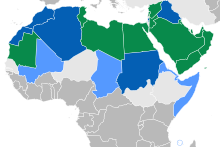
Use of Arabic as the national language (green), as an official language (dark blue) and as a regional/minority language (light blue)
|
|
| This article contains IPA phonetic symbols. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols instead of Unicode characters. For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. | |
Arabic (اَلْعَرَبِيَّةُ, al-ʿarabiyyah [al ʕaraˈbijːa] (![]() listen) or عَرَبِيّ, ʿarabīy [ˈʕarabiː] (
listen) or عَرَبِيّ, ʿarabīy [ˈʕarabiː] (![]() listen) or [ʕaraˈbij]) is a Semitic language that first emerged in the 1st to 4th centuries CE.[3] It is now the lingua franca of the Arab world.[4] It is named after the Arabs, a term initially used to describe peoples living in the Arabian Peninsula bounded by eastern Egypt in the west, Mesopotamia in the east, and the Anti-Lebanon mountains and Northern Syria in the north, as perceived by ancient Greek geographers.[5] The ISO assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form, Modern Standard Arabic,[6] also referred to as Literary Arabic, which is modernized Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as al-ʿarabiyyatu l-fuṣḥā (اَلعَرَبِيَّةُ ٱلْفُصْحَىٰ[7] "the eloquent Arabic") or simply al-fuṣḥā (اَلْفُصْحَىٰ). Modern Standard Arabic is an official language of 26 states and 1 disputed territory, the third most after English and French.[8]
listen) or [ʕaraˈbij]) is a Semitic language that first emerged in the 1st to 4th centuries CE.[3] It is now the lingua franca of the Arab world.[4] It is named after the Arabs, a term initially used to describe peoples living in the Arabian Peninsula bounded by eastern Egypt in the west, Mesopotamia in the east, and the Anti-Lebanon mountains and Northern Syria in the north, as perceived by ancient Greek geographers.[5] The ISO assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form, Modern Standard Arabic,[6] also referred to as Literary Arabic, which is modernized Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as al-ʿarabiyyatu l-fuṣḥā (اَلعَرَبِيَّةُ ٱلْفُصْحَىٰ[7] "the eloquent Arabic") or simply al-fuṣḥā (اَلْفُصْحَىٰ). Modern Standard Arabic is an official language of 26 states and 1 disputed territory, the third most after English and French.[8]
Arabic is widely taught in schools and universities around the world and is used to varying degrees in workplaces, governments and the media.[9] Arabic, in its standard form, is the official language of 26 states, as well as the liturgical language of the religion of Islam, since the Quran and the
| Рубрики: | Arabic |
Понравилось: 1 пользователю
| Комментировать | « Пред. запись — К дневнику — След. запись » | Страницы: [1] [Новые] |






